· GoodSleep Team · sleep-hygiene-habits · 3 min read
10 Science-Backed Tips for Better Sleep Quality

Introduction
Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for your physical and mental health. If you’re struggling to get the rest you need, these 10 evidence-based tips for better sleep can help you establish healthier sleep habits. Quality sleep affects everything from cognitive performance to emotional regulation, making sleep improvement a vital component of overall wellness. These sleep hygiene practices have been shown to significantly improve sleep quality, reduce sleep disorders, and enhance your sleep-wake cycle.
Understanding your unique sleep needs and implementing consistent sleep routines are foundational steps toward better sleep. Whether you’re dealing with occasional insomnia, sleep disruption, or simply want to optimize your sleep quality, these strategies address key factors that influence your ability to fall asleep, stay asleep, and wake up feeling refreshed.
The Tips
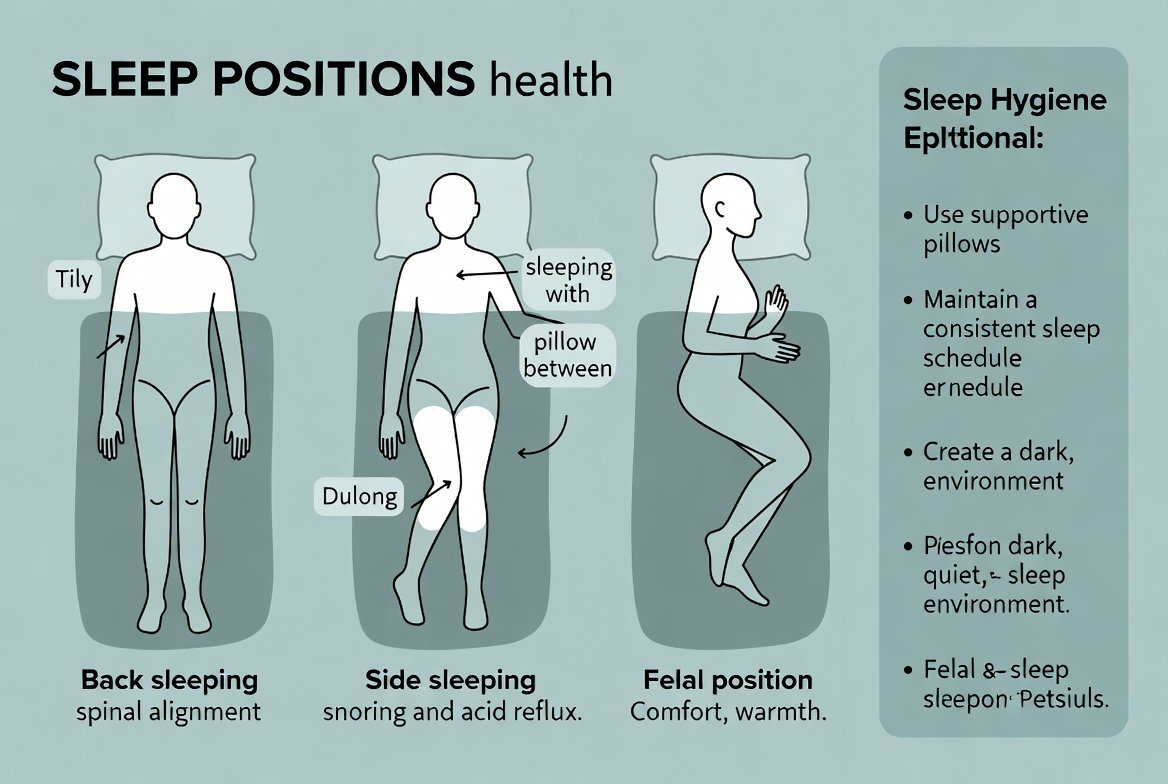
- Stick to a Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Wind down before bed with activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music. Avoid screens for at least an hour before sleep.
- Optimize Your Bedroom Environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, cool, and comfortable. Consider blackout curtains, earplugs, or a white noise machine.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Avoid caffeine in the late afternoon and evening, and limit alcohol consumption, especially close to bedtime, as both can disrupt sleep.
- Avoid Large Meals Before Bed: Eating heavy meals too close to bedtime can cause discomfort and indigestion, making it harder to fall asleep.
- Get Regular Exercise: Physical activity during the day can promote better sleep at night. However, avoid intense workouts too close to bedtime.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Limit Naps: If you must nap, keep it short (20-30 minutes) and in the early afternoon to avoid interfering with nighttime sleep.
- Avoid Screens Before Bed: The blue light emitted from phones, tablets, and computers can suppress melatonin production, a hormone that helps you sleep.
- Consult a Professional: If you consistently struggle with sleep despite trying these tips, consider talking to a doctor or sleep specialist.
Understanding Your Sleep Needs
Every person has unique sleep requirements based on age, lifestyle, and individual factors. While adults typically need 7-9 hours of sleep per night, the quality of that sleep is just as important as the quantity. Factors such as sleep stages, sleep cycles, and circadian rhythm alignment all contribute to how rested you feel upon waking.
Sleep Disorders and When to Seek Help
If you consistently struggle with sleep despite implementing these healthy sleep habits, you may have an underlying sleep disorder such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or chronic insomnia. Common signs include loud snoring, frequent awakenings, excessive daytime sleepiness, or difficulty maintaining sleep for more than a few weeks.
Sleep Tracking and Monitoring
Consider using sleep tracking tools to better understand your sleep patterns. These tools can reveal insights about your sleep stages, sleep efficiency, and factors that might be affecting your sleep quality. Knowledge about your personal sleep patterns can help you make more targeted improvements.
Conclusion
Implementing even a few of these evidence-based tips for better sleep can make a significant difference in your sleep quality and overall health. The key is consistency and finding the right combination of sleep hygiene practices that work for your lifestyle and individual needs.
Remember that sleep improvement is a gradual process. Focus on building sustainable sleep habits that support your circadian rhythm and create an environment conducive to restorative rest. Sweet dreams!